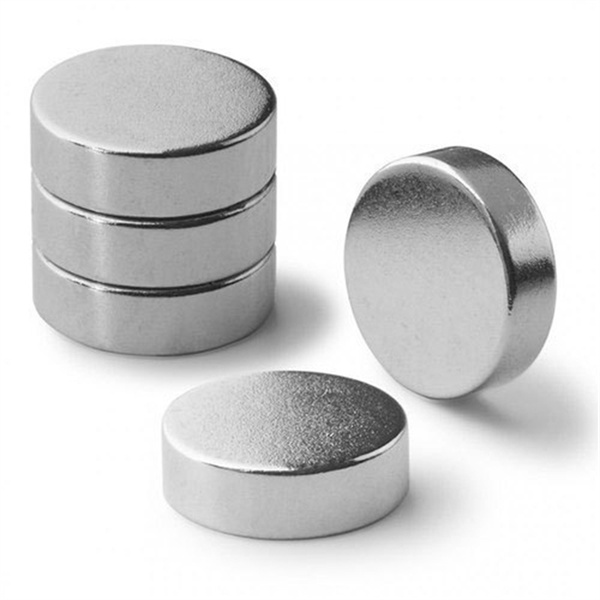
N45 Disc Magnets Neodymium Permanent Disc Magnet
N45 Disc Magnets Neodymium Permanent Disc Magnet
Magnets Display




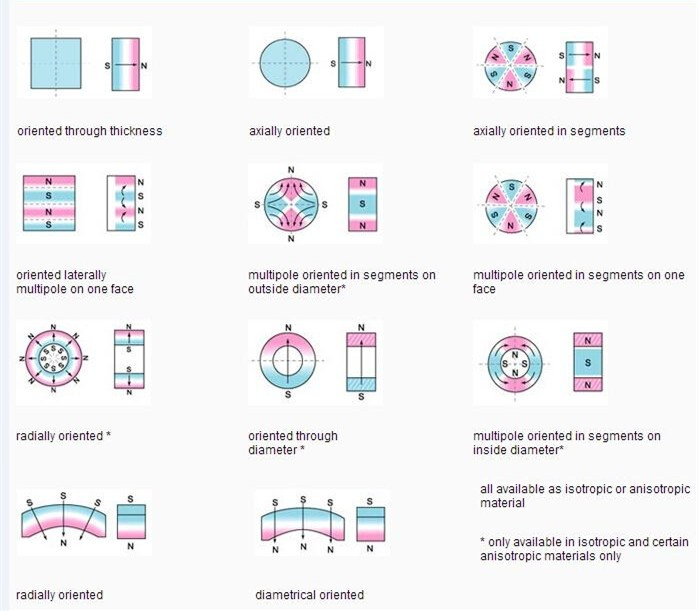
Magnetic Direction
he north pole is defined as the pole of a magnet that, when free to rotate, seeks the north pole of the earth. In other words, a magnet's north pole will seek the earth's north pole. Similarly, the south pole of a magnet seeks the south pole of the earth.
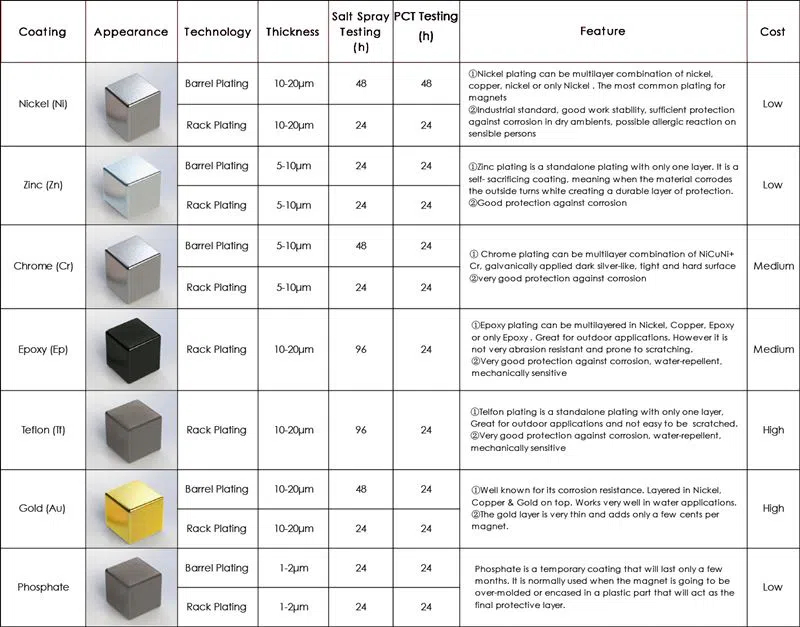
Coating
Our Strength



What are magnets made of
Modern permanent magnets are made of special alloys that have been found through research to create increasingly better magnets. The most common families of permanent magnet materials today are made out of aluminum-nickel-cobalt (alnicos), strontium-iron (ferrites, also known as ceramics), neodymium-iron-boron (a.k.a. neodymium magnets, or "super magnets"), and samarium-cobalt-magnet-material. (The samarium-cobalt and neodymium-iron-boron families are collectively known as the rare-earths).
PRODUCT CATEGORIES
Focus on providing magnets solutions for 30 years
















